
Typical Treatment
– Cryopreservation
Cryopreservation-Embryo or Oocyte
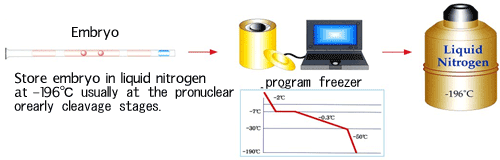
They are frozen slowly at an electronically controlled rate in the presence of a cryoprotectant and stored in the liquid nitrogen at the 4~6 cells stages.
Reasons for cryopreservation are (i) to keep surplus fentilized embryos for possible future implantation, (ii) to avoid ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, (iii) to azoid multiple pregnancies (iv) to increase the chanses of implantation success (v) to store the intact oocytes of woman who may suffer irreparable ovarian damage due to chemotherapy or irradiation.
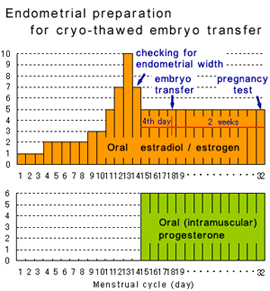
Cryo-thawed embryo transfer in:
1. natural cycle
2. Hormone-replaced cycle
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
| Natural cycle |
|
|
| Hormone-replaced cycle |
|
|
Cryopreservation-Sperm
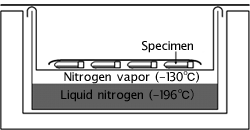 The separated sperm from seminal plasma by density gradients are mixed with a cryoprotedtant and are then loaded into liquid nitrogen vapor to freeze, before plunging into liquid nitrogen.
The separated sperm from seminal plasma by density gradients are mixed with a cryoprotedtant and are then loaded into liquid nitrogen vapor to freeze, before plunging into liquid nitrogen.
